Appearance
Exercise 2 - Create a Meeting Notes Summary Prompt Template
Prompt Engineering Introduction and Terminology
Prompt engineering means figuring out how to ask a question to get exactly the answer you need from a Large Language Model. It’s carefully crafting or choosing the input (prompt) to get the best possible output.
- What it means for customers: When your generative AI tool gets a strong prompt, it’s able to deliver a strong output. The stronger, more relevant the prompt, the better the end user experience.
- What it means for teams: Can be used to ask a large language model to generate a personalized email to a customer, or to analyze customer feedback and extract key insights.
Prompt Engineering: Best Practices
Instruction Clarity
- Directives: The explicit commands or instructions given in the prompt. The clearer and more direct these are, the better the model can align its output with the intended task.
- Example: "Translate the following text to French" is a clear directive, whereas "What is this text in French?" is less direct and could result in varied interpretations.
Context Length and Content
- Prompt Length: The length of the prompt, which includes both the instructions and any context provided. Large language models like GPT-3 and GPT-4 have token limits (e.g., 4,096 tokens for GPT-3.5), which include both the input and output. This means that the length of the prompt directly affects how much room is left for the model’s response.
- Context Embedding: The practice of embedding relevant background information within the prompt to guide the model’s understanding. This can involve providing specific facts, prior conversations, or structured data.
- Example: "Given that X is true, explain Y" where "X" is the embedded context.
Output Specification
- Expected Output Type: Defining the format or type of response expected, e.g. a list, a paragraph, a code snippet. This helps the model understand not only what to generate but also how to structure the output.
- Length Constraints: Specifying a desired output length, either in terms of word count, sentences, or tokens. This constraint is particularly useful when space is limited or when concise responses are necessary.
- Example: "Summarize in 150 words" vs. "List five key points."
Types of LLMs
Large Language Models can be categorized into general-purpose models, customer-specific models, industry-specific models, and small language models. Each type has distinct applications and is best suited for specific business needs. Make sure to review our LLM Benchmark for CRM at https://www.salesforceairesearch.com/crm-benchmark
Model Integration
Various LLMs can be used in combination to achieve better outcomes. For example, customer-specific models may be integrated with industry-specific models to provide more tailored and effective solutions. Small language models can also complement larger models in scenarios where efficiency and speed are crucial.
Step 1: Create a Meeting Notes Summary Prompt Template
Now let's draft a prompt template that will summarize meeting notes. To do this, we will write clear instructions that describe what is needed from the LLM. And we’ll also ground the prompt using Salesforce’s data model as well as using flows.
- Click the Setup gear icon and click Setup. (Or, If you are still in agent builder, click the “Back” arrow at the top-left)

- In the quick find box, type Prompt, then click Prompt Builder.
- Click on the New Prompt Template button on the top right corner of the page.

- Enter the details below:
- Select Flex for Prompt Template Type.
- Prompt Template Name:
Summary Meeting Notes - Template Description:
Extract and Summarize Meeting Notes provided by the user - Define Source
- Name: Meeting Notes - don’t make changes to API NAME
- Source Type: Free Text
- Click Next.
- Let’s add our prompt text. Copy and paste the following text into the Prompt Template Workspace:
You are a sales representative who has just concluded a meeting with a client.
Based on the meeting note description {!$Input:Meeting_Notes} identify the
following sections: People, what was discussed, next steps, client requirements,
potential opportunities and summarize each of the sections. Also, rename the
sections to be professional and use a bulleted format.
This should not be in an email format. This is to be saved in meeting notes and
opportunity next steps.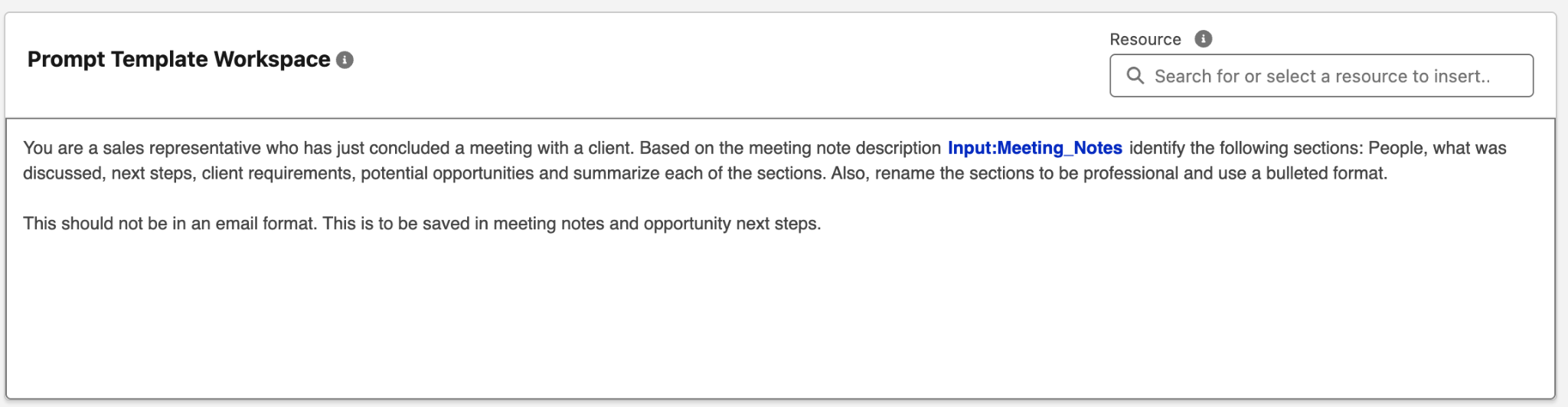
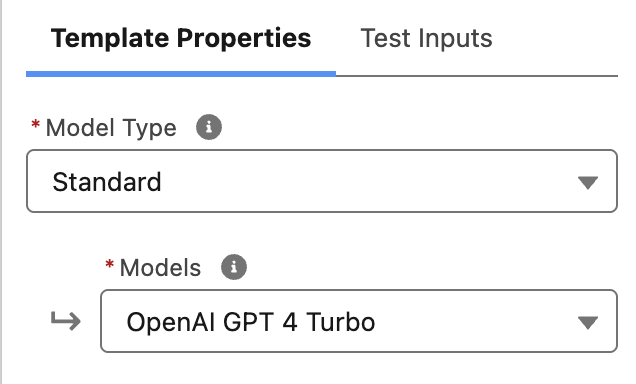
- On the right side under Template Properties for Models, select OpenAI GPT 4 Turbo.
- On the right side under Test Inputs paste the following:
Take Note Met with Chris Post & Lauren Bailey at Omega Inc. Great discussion
around regulatory compliance challenges. This is a potential to position our
Regulatory Advisory Services opportunity of $3000000. The client would like to
start project by May 15th.In the Lower Preview section, click Preview

The Response Section of the prompt will showcase the expectations it has identified. Like this:

If everything works smoothly, Activate your new prompt template.
Test your prompt with your own version of the meeting notes to see if it is able to recognize client expectations.
Change the output format to paragraph by asking the prompt to generate a client expectation summary as a professionally written paragraph
Example: Let’s add our prompt text. Copy and paste the following text into the prompt template:
You are a sales representative who has just concluded a meeting with a client. Based on the meeting note description {!$Input:Meeting_Notes} identify the following sections: People, what was discussed, next steps, client requirements, potential opportunities and summarize each of the sections. The output should be in paragraph format that can be sent in an email to the client.
This completes Exercise 2.
